Is Clay Soil Acidic Or Alkaline? (Fixing pH Like a Pro!)

Plants have various tolerances when it comes to soil pH.
While some plants prefer acidic conditions, others are better off in an alkaline environment. However, knowing what you’re working with is essential.
So if you have clay in your garden, it’s useful to know whether clay soil is acidic or alkaline?
Let’s find out…
Is the pH of Clay Soil Acidic Or Alkaline?
Soil chemistry is a product of various conditions, but on the whole, clay soil is mild to highly alkaline, with a pH range of 8 to 10. Higher alkalinity often has detrimental effects on plants, which is one of the reasons clay soil needs amending.
What Is The pH Of Clay Soil?
For all soil types, the pH scale runs from 0 to 14. Neutral is represented by the value 7. Anything above that (7.5 and up) is considered alkaline or a “base.” Anything below is acidic. Clay soil has a pH in the mid-upper range (between 8 and 10).
To put this into perspective:
- Battery acid has a 0 pH rating according to the scale,
- Very alkaline substances include bleach (roughly 13.5 pH) and drain cleaner with a pH of 14 (potent stuff, especially if you spill some on your finger)
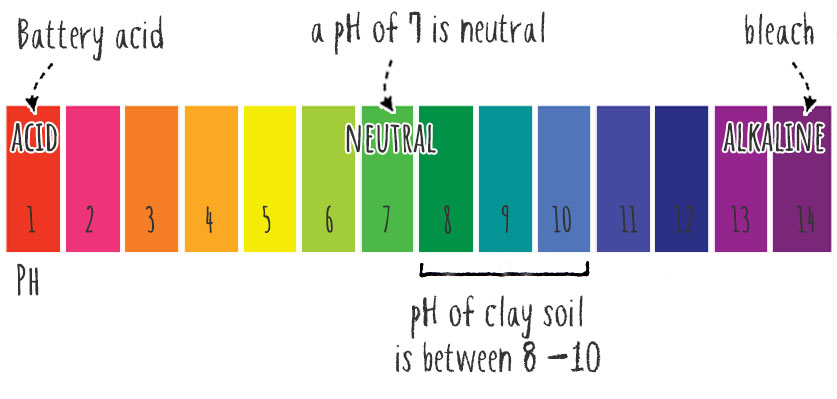
As you can see from these extreme examples, the closer the soil is to a pH of 7, the “better” it is at facilitating growth because it’s less caustic.
For comparison, sandy soil has a more acidic pH, while loam soils are neutral.
How Does Clay Affect Soil pH?
While plants benefit significantly from a balance of soil particles, too much clay in the ratio results in an alkaline environment; most plants enjoy a soil pH of between 5 and 7.
Unfortunately, clay is generally inhospitable for many plants because the high alkalinity reduces the plants’ ability for nutrient uptake (plants struggle to absorb nutrients from the soil in high alkaline conditions).
In essence, plants become starved of essential nutrients, including:
- Iron
- Magnesium
- Nitrogen
- Phosphorus
What Causes Clay Soil’s Alkalinity?
Clay soil is naturally high in pH-increasing compounds, including sodium carbonate (Soda ash), calcium carbonate, and sodium bicarbonate.
- Calcium carbonate has a pH of roughly 11.
- Sodium carbonate has a pH of between 10 to 11.
- Sodium bicarbonate has a pH of between 8 and 9.
This is because clay soil is excellent at retaining water and other minerals (like salts), thanks to the small particle sizes that limit the amount of water passing through (clay particles are less than 0.005 millimeters in diameter).
For example, sodium carbonate (in the presence of water) binds to free-floating hydrogen molecules, making them unavailable. The less free hydrogen, the more the pH score increases.
So, How Do You Make Clay Soil More Acidic?
While some plants are alkaline tolerant, most plants are not. Gardeners spend considerable sums trying to alter the pH value of the soil.
However, before you add chemicals or natural soil-restoring products, you must know what the pH of your garden soil is and how much it needs to change.
Testing Clay Soil pH
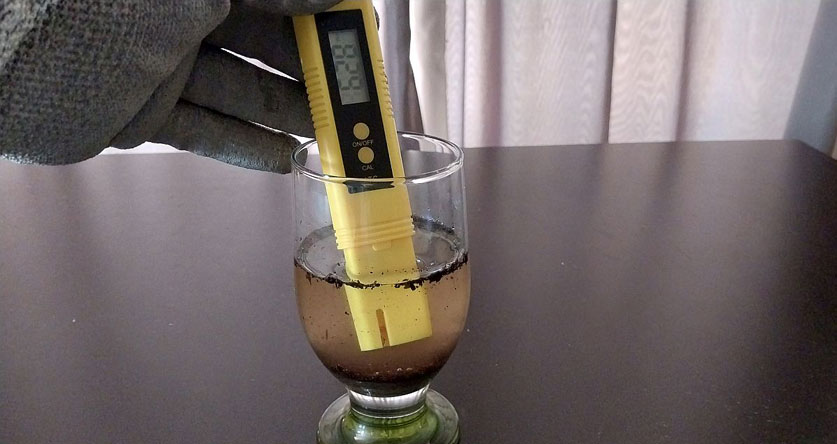

The only way to be sure about the pH of your clay soil is to perform a pH test with an adequate testing kit like this (Amazon). However, if you’re cash-strapped, you can use some basic kitchen supplies to gain a rough understanding of what your garden’s pH is.
Try these methods to test:
- Start by collecting a soil sample ( dig roughly 4 to 6″ below the surface with a hand trowel). You’ll need to take several samples from different areas in your garden to find the average.
- Once collected, break apart large clumps and remove debris like sticks and stones.
- Next, mix roughly one cup of mixed soil with enough water to create a slurry (mud). The water should be distilled to prevent contamination.
- Test for alkaline conditions by adding ½ cup vinegar to the mix. If the mud bubbles or foams, it is alkaline. If there is no reaction, try the process again.
- Test for acid conditions by following the same process (with “clean soil”). Add ½ cup of baking soda this time and wait for the reaction. If there is none, try again. If it bubbles or foams, your soil is acidic.
While this method helps you identify acid or alkaline conditions, more is needed to give accurate readings. Store-bought test kits offer a more precise alternative.
You have a few different testing options available:
- You could try an electronic meter
- Special chemical kits like this
- I prefer to use litmus paper (simple & cheap!)
(Amazon links)
Using a pH testing kit
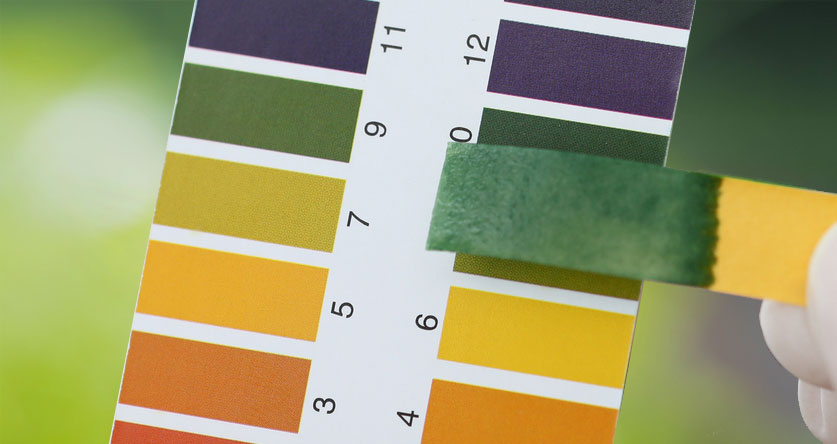

- After collecting samples, mixing them, and removing the debris, you’ll mix roughly 3 teaspoons of soil with enough water (preferably distilled) to cover the sample. You’ll need to mix the mud and let it stand for around 30 minutes.
- Filter the solution through filter paper (coffee filters work well) and collect the liquid in a separate (clean) container. Then, add a piece of litmus (pH testing) paper to the liquid.
- The kit the paper came with will give you a color chart to compare the results.
In severe situations, I recommend taking your soil sample to a laboratory to be accurately tested.
The ideal pH range for most soils is between 5.5 and 7.5. Remember that conditions can vary over time, so regularly testing your soil’s pH (at least once a year) is important.
Tip: Many gardeners prefer to test their soil in the fall, allowing them enough time to fix any discrepancies before the growing season starts in the spring.
How To Reverse The Alkalinity In Heavy Clay Soil?
So, now that you’ve figured out the scope of your situation, you’ll need to intervene in clay-dominant soils to correct the pH imbalance.
There are two main intervention routes to reversing the alkaline levels :
- Adding chemicals
- Adding organic materials
Neither method is purely good or bad, as both have pros and cons…
Using Compost To Increase Soil Acidity
Adding compost to the soil is always a good idea. It improves the soil structure, adds nutrients, and (depending on the compost type) can help reduce the alkalinity.
As you can probably guess, this is my preferred method!
Some examples of beneficial compost include those made using manure, pine needles, and wood ash. The downside is that these are slow-acting, and they may not have the “impetus” to break highly alkaline soils.
The benefit is that mixing compost into the soil breaks up the compacted clay, vastly improving the soil structure. Compost also generally has the least adverse side effects.
Using Coffee Grounds
Like compost, coffee grounds add structure to the soil (when mixed in and during decomposition). Thanks to the naturally occurring acid in coffee, these grounds help to reduce the alkalinity, but only slightly.
They are more beneficial for maintaining a lower pH.
Using Mulch To Increase Soil Acidity
The difference between mulch and compost is that mulch sits on top of the soil and assists in water retention while leaching nutrients.
Once again, you’ll need to find an acidic mulch as they come in different “strengths.”
Pine needles, oak, and maple leaves make excellent mulch/leaf mold! They are full of essential bacteria and produce acidic leachates.
Increase Soil Acidity With Vinegar Or Lemon Juice
When you need to lower the pH quickly but don’t want to use potentially hazardous chemicals, add diluted vinegar to the soil (or lemon juice).
Thanks to the naturally occurring acid in these liquids, they begin to alter the pH.
Agricultural vinegar has a 20% acid concentration and is quite effective for extreme alkalinity. However, increasing the dose in smaller increments is better before diving in with the hard stuff. The diluted solution should have a pH of roughly 2.7. You can use a watering can for application.
Use Aluminum Sulfate, Elemental Sulfur, Or Sulfuric Acid
If your soil is considerably alkaline (above 8), you may be tempted to bring in the “big guns.” While these chemicals are potent, they are also dangerous.
Sulfuric acid, for example, is battery acid, which will drastically reduce the pH but render the soil unusable for a time. Most home gardeners are discouraged from attempting to use it.
Fortunately, aluminum sulfate and elemental sulfur are standard options for home gardeners. Aluminum sulfate is more soluble and faster-acting. However, it is more expensive than elemental sulfur. When I have to revert to this kind of solution, I prefer organic elemental sulfur. (Amazon)
How To Maintain Acidity Levels In The Soil
While adding chemicals to the soil may adjust the pH to a more suitable level in the short term, it is unfortunately not a long-term solution. The only way to alter the pH with lasting consequences is to improve the soil structure of the previously clay-dominant area.
Once the pH is under control, I recommend taking up a regular composting routine.
The quintessential factor is to test the soil’s pH before and after and then to maintain it annually.