Plants That Don’t Like Mushroom Compost (Good or Bad?)

Most of the time, mushroom compost is highly beneficial for plants.
But this type of compost has a slightly different chemical composition, which for some plants can be problematic.
So even if you think you’re doing your garden some good, a few plants just don’t like mushroom compost.
keep reading to find out how to work around this problem, and understand which plants to avoid using with mushroom compost…
Is mushroom compost good for all plants?
Some plants do not do well at all when mushroom compost is used. This is because of two noticeable characteristics of mushroom compost. Salinity and alkalinity. In other words, the concentration of salts and the pH level of the compost.
Mushroom compost typically contains high levels of salt. Salt absorbs water, but plants also need moisture for healthy growth.
Suppose you notice plant leaves wilting and turning yellow-brown. In that case, mushroom compost may be causing “leaf burn” (also known as “leaf scorch” because foliage ends up looking burned at the edges). This happens because the salinity of the compost reduces the availability of water for the plant’s tissues.
Notice that this can also happen when you over-fertilize plants since fertilizers are mostly made up of salts.
One of the other common concerns about mushroom compost is its alkalinity (primarily since gypsum or lime is used as part of the compost ingredients).
For this reason, most gardeners recommend avoiding the use of mushroom compost with acid-loving (ericaceous) plants.
However, most studies I have read show that mushroom composts are relatively neutral, with a pH level of about 6.6 to 7.
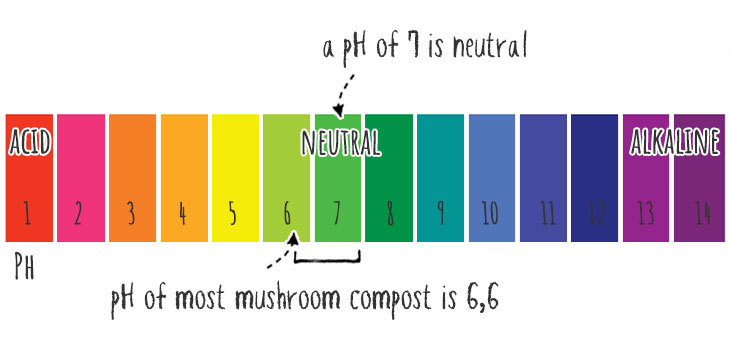
The pH scale measures how acid or alkaline a substance is. The scale ranges from 1 to 14, with 7 being considered neutral.
So you probably wouldn’t want to use this on “lime-hating” plants, preferring a more acidic type of compost. Still, in most other applications, the alkalinity isn’t a problem.
Even if mushroom compost starts off with a fairly neutral pH, the main reason for avoiding it is its “liming effect” (because of the lime is used in its ingredients).
Lime lowers the acidity of the soil! (makes it more alkaline).
A simple soil tester like this one will give you a better understanding of your soil’s existing acidity. (Amazon link)
Where should you not use mushroom compost?
Of these two characteristics, salt levels are perhaps the biggest concern.
Before using mushroom compost, check whether your plants are “salt-sensitive” or “salt-tolerant.” Salt tolerant plants will be better at absorbing water from their environment.
But the most important thing to keep in mind is that mushroom compost is a rich form of compost with a high quantity of organic matter. The most significant ingredient in mushroom compost is straw and hay. And only a small amount is gypsum or manure.
This produces nutrient-rich compost, which is an excellent soil amendment. The key to using it is more about the quantity used.
Applying it in small amounts will help build a good soil structure and provide soil nutrients. Another good habit is to use mushroom compost before the growing season. Leaving it in the soil for a couple of months will help cure the compost, and some of the soluble salts will leach away.
As a general rule, mix mushroom compost well with your soil. Using a 1 part to 3 parts ratio is a good starting point (25% compost to 75% soil).
What plants don’t like mushroom compost

All plants have varying levels of sensitivity to soluble salt and alkalinity. Some plants that don’t like salty soil conditions or prefer a more acidic soil substrate are listed below:
Fruit and veg plants:
- Blueberries
- Cranberries
- Gooseberries
- Juniper
- Peppers
- Radishes
- Raspberries
- Rhubarb
Decorative plants:
- Azaleas
- Aster
- Begonias
- Camelias
- Daffodil
- Ferns
- Gardenia
- Heather
- Holly
- Iris
- Japanese maple
- Hydrangeas
- Magnolia
- Nasturtium
- Rhododendrons
Is mushroom compost good for seedlings or potted plants?

This is an important thing to remember. Mushroom compost can be harmful to young plants and seedlings. This is because the soluble salts and other nutrients supplied by mushroom compost are too much for germinating plants.
Studies have shown that the growth of seedlings slows down in mushroom compost.
What plants like mushroom compost
Remember that mushroom compost is suitable for most vegetables, flowering plants, and herbs. Here are a few plants that work well with mushroom compost. These are more “lime-loving” and salt-resistant plant types:
- Agapanthus
- Acacia
- Aeoniums
- Butterfly weed
- Chinese silver grasses
- Columbine
- Gazania
- Hibiscus
- Honeysuckle
- Junipers
- Lavender
- Lilac
- Ornamental clovers
- Polemoniums
- Prickly pear cactus
- Sea holly
- Sea thrift
Is mushroom compost good for my garden?
To put things in context, the soluble salts in mushroom compost are lower and more stable than most fertilizers. Nevertheless, matching the application rate to each plant’s requirements is essential.
Also, you need to be aware of the starting point for your soil? For example, is it alkaline or acid? Do you have chalky soil?
Using a soil tester like this one will give you a better understanding of your soil’s existing condition. (Amazon link)
In general, avoid using mushroom compost if your soil is already chalky and alkaline.
The best practice is to use mushroom compost in small amounts and avoid plants that might be sensitive to salt or alkalinity.
FAQ – What is mushroom compost good for?
Mushroom compost has a wealth of benefits, including:
- As a soil amendment: to improve soil structure and fertility.
- Nutrient enrichment: this rich organic matter contains essential nutrients
- pH balancing: it is slightly alkaline and helps balance acidic soils.
- Disease suppression: some reports have shown disease preventive properties.
- Mulching: mushroom compost makes great mulch and adds organic matter to the soil when it breaks down.
Here are a few of the more common questions people ask about mushroom compost and plant compatibility:
Is mushroom compost good for vegetables?
Yes, mushroom compost is fantastic for the majority of vegetables, especially since foo crops don’t like acid soil conditions. In addition, the liming effect of mushroom compost could be beneficial for vegetable gardens.
Is mushroom compost good for fruit trees?
A lot of fruit plants prefer acid to neutral soil conditions. Therefore, you would be better off using ericaceous compost for nurturing fruit trees.
Is mushroom compost good for lawns?
Most grass varieties for lawns are salt-tolerant. So if you live in a region close to the coast, you most probably have a salt-resistant lawn.
Mushroom compost can be used as a soil amendment for lawns of most types, especially since you only need a minimal amount.
You only need a ¼ to ½ inch turf dressing for established lawns.
Do roses like mushroom compost?
The ideal pH of soil for growing roses is said to be 6,5. This is the average level of most mushroom composts. So mushroom compost makes a good soil amendment for growing roses.
Roses vary in their levels of salt resistance, but most varieties are moderately salt-tolerant. As in most situations, use compost in moderation.
Do cucumbers like mushroom compost?
Yes. Because mushroom compost is calcium-rich, this can help cucumber plants’ healthy growth and yield. In addition, studies have shown mushroom compost to be beneficial for the quality of cucumber plants.
Is mushroom compost good for tomatoes?
Yes, mushroom compost is good for tomatoes. Although tomato plants generally prefer acidic soils, they are also moderately salt tolerant. Also, the calcium content in mushroom compost can benefit tomato plants.
Use mushroom compost as a mulch in small quantities on tomato plants.
Is mushroom compost good for strawberries?
Used as a mulch, mushroom compost is effective for growing strawberries. Strawberries need plenty of moisture for healthy growth, and the mulch will help retain water. And strawberries are also one of the most salt-tolerant fruit crops.